The Ultimate Guide to Google Maps Scraping for Lead Generation
Table of Contents
How Local Businesses Can Use Google Maps Scraping to Find More Customers
Google Maps Scraping is quickly becoming one of the most powerful tactics for local businesses that want to uncover new leads, monitor competitors, and improve their online visibility.
Data shows that every day, millions of people use Google Maps to find shops, services, and restaurants nearby. Behind every map pin is a huge repository of public business data. Data that includes business names, phone numbers, websites, ratings, and reviews. With this data, you can make smarter marketing decisions.
The problem? Google Maps wasn’t built for large-scale data collection.
Manually copying information from a listing takes hours, is impossible to scale, and even the official Google Maps API limits you to 60 results per search, which makes it more expensive and inefficient for lead generation.
That’s where Google Maps Scraping tools come in.
Platforms like Outscraper, Apify, Octoparse, PhantomBuster, and ScraperAPI can automatically extract thousands of business listings in minutes. You’ll get structured data in CSV, Excel, or JSON format. With these popular formats, you’re now ready to filter, segment, and import this data into your CRM or email campaigns. Most no-code Google Maps scraping platforms offer API and integration tools to make your job even easier.
Of course, scraping Google Maps technically violates Google’s Terms of Service, and the platform actively detects automated data extraction. That’s why using these tools responsibly and focusing only on publicly available data is crucial. These extraction tools can unlock enormous marketing value
What You'll Learn in This Guide
This guide walks you step-by-step through everything you need to know about Google Maps Scraping, from fundamentals to practical implementation.
- Defining Google Maps Scraping: You’ll learn what Google Maps Scraping actually is, how it automates data collection, and why it’s far more efficient than manual research.
- The Extensive Value of Google Maps Data: We’ll explore how Google Maps has evolved into a global business database, covering 250+ countries, 200 million businesses, and over a billion active monthly users.
- Why Businesses Scrape Google Maps: Discover how scraping powers lead generation, market research, competitor tracking, and local SEO insights with real-world examples of how companies use this data to boost growth.
- What You Can Retrieve or Data Extraction Capabilities: From basic info like names and phone numbers to advanced data like reviews, ratings, and geo coordinates. We’ll break down everything you can extract (and how to use it).
- Methods for Data Extraction and Comparing Approaches: We’ll compare manual collection, the Google Maps API, and automated scraping tools (Outscraper, Apify, Bright Data, Octoparse, & ScraperAPI) as well as custom Python scrapers.
- Technical and Legal Compliance: You’ll learn how to stay compliant while scraping, how to use proxies responsibly, and how to understand Google’s anti-scraping methods, while following GDPR-friendly best practices.
- Driving Data-Informed Decisions: Finally, we’ll show you how to integrate scraped data into your CRM, marketing stack, or SaaS tools (like Zapier, Make, & N8N) to drive smarter, data-backed decisions.
Why This Guide Matters
By the end, you’ll know exactly how to use Google Maps Scraping to:
✅ Build targeted local lead lists in minutes
✅ Analyze your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses
✅ Identify new areas for expansion
✅ Personalize your marketing with real, verified business data
In short, Google Maps Scraping isn’t just a data hack but a growth strategy that turns free, public data into actionable business intelligence.
What is Google Maps Scraping
Defining Google Maps Scraping
Google Maps scraping is the automated process of extracting business data from Google Maps using specialized software tools. Instead of spending countless hours manually copying and pasting details like business names, addresses, phone numbers, ratings, and websites, scraping tools handle this task at scale, faster, accurately, and efficiently.
These tools gather structured data directly from Google Maps search results and export it into user-friendly formats such as CSV, JSON, or Excel. With this structured data, marketers and business owners can instantly build lists, analyze local competitors, and identify new market opportunities without writing a single line of code.
Google Maps scraping replaces repetitive manual work with automation, turning what used to take days into a matter of minutes.
The Extensive Value of Google Maps Data
Google Maps is not just a navigation tool, but it’s one of the largest, most valuable business data sources on the planet.
According to Alphabet, the parent company of Google, Maps now covers 250 countries and territories, hosts data on 200 million businesses, and serves more than 1 billion monthly users.
This makes a living, breathing database of the global business world, from small local shops to multinational chains. Unlike social platforms that require logins or private access, Google Maps is publicly accessible, offering up-to-date business information to anyone, anywhere in the world.
For marketers, sales teams, and data-driven entrepreneurs, this accessibility transforms Google Maps into the most valuable lead generation asset, local SEO research, and market intelligence.
By tapping into this data responsibly (and within ethical and legal limits), businesses can uncover actionable insights such as:
- Which competitors dominate certain locations
- What niches are underserved in specific cities
- Where potential clients are most concentrated
Understanding Google Maps is very important, and business owners should realize that Google Maps Scraping turns a navigation app into a global business discovery engine.
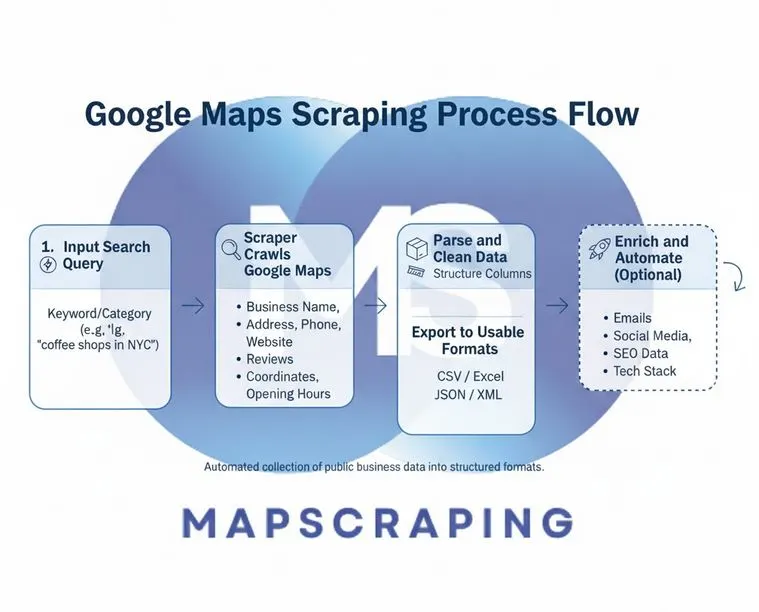
How Google Maps Scraping Works
Google Maps Scraping automates the process of collecting publicly available business data directly from Google Maps and exporting it into structured formats. It replaces hours of manual copy-pasting with powerful tools that can gather thousands of listings in minutes.
Step-by-Step Process Flow of Google Maps Scraping:
- Input Search Query: You start by entering a keyword or business category. For example, “coffee shops in New York” or “real estate agencies in California”.
- Scraper Crawls Google Maps Results: The scraper automatically go through Google Maps search results, collecting data such as:
- Business Name
- Address and postal code
- Phone number
- Website URL
- Reviews and ratings
- Coordinates (latitude/longitude)
- Opening hours
- Parse and Clean Data: The raw HTML data is processed, duplicates are removed, irrelevant tags are filtered, and information is structured into clean columns for analysis.
- Export to Usable Formats: Once cleaned, the data is exported into easy-to-use formats like:
- CSV / Excel (for CRMs or spreadsheets)
- JSON / XML (for developers or automation tools)
- Enrich and Automation (Optional): Some advanced scrapers connect to enrichment tools to add:
- Emails or professional networking sites’ profiles
- Social media pages
- SEO data (meta titles, keywords)
- Advertising pixels or website tech stack
Visual Process of Google Maps Scraping
Common Tools for Google Maps Scraping
| Method | Best For | Example Tools |
|---|---|---|
| No-Code Platforms | Beginners, marketers | Outscraper, Apify, Octoparse |
| APIs | Scalable projects | Bright Data, Scrapingdog, ScrapeAPI |
| Custom Code (Python) | Developers needing flexibility | Selenium, BeautifulSoup, Playwright |
Why Business Scrape Google Maps Data
Google Maps Scraping isn’t just about collecting data, but it’s about uncovering strategic insights that drive smarter sales, marketing, and business decisions. When executed responsibly, it converts the world’s most comprehensive business directory into a competitive growth engine.
Superior Lead generation
One of the most powerful use cases of Google Maps scraping is lead generation, especially for local and B2B businesses.
Instead of manually searching for prospects, scraping tools compile detailed business listings of business names, phone numbers, websites, and even ratings into a single, unified database.
This process allows teams to:
- Build highly targeted prospect lists for outreach and CRM integration.
- Compile fragmented business information (emails, URLs, categories) into one lead database.
- Improve local B2B lead generation. This is ideal for real estate, SaaS, marketing agencies, or event organizers.
- Personalize outreach at scale by segmenting based on pain points (e.g., finding low-rated restaurants to pitch reputation management tools).
In-Depth Market Research and Location Intelligence
Beyond lead generation, Google Maps scraping enables precise market research and location-based analysis.
It empowers companies to understand where competitors are, which markets are overserved or underserved, and where expansion makes the most sense.
Businesses use scraped data to analyze market saturation, benchmark local competitors, perform geospatial analysis, track customer traffic, and support academic, urban planning, and engineering studies.
With Google Maps’ global coverage and real-time updates, it offers a dynamic layer of location intelligence that a static database can’t match.
Proactive Competitor and Sentiment Analysis
In competitive industries, Google Maps scraping provides deep insights into how rival businesses perform from their ratings, review patterns, and pricing strategies.
Through scraped data, companies can monitor competitor activity, openings, and closures; evaluate brand sentiment by analyzing positive and negative reviews at scale; identify common complaints and use them to enhance product positioning; and benchmark performance by region, rating distribution, or customer feedback volume.
Enhanced Marketing Strategies and Business Growth
Finally, Google Maps scraping could be used to improve precision marketing and data-driven growth strategies.
By extracting accurate, real-time data (including reviews, locations, and contact details), marketers can:
- Create hyper-local ad campaigns tailored to geography, business size, or review sentiment.
- Identify partnership opportunities with complementary nearby businesses.
- Automate email or cold outreach using verified contact data.
- Enhance personalization by targeting businesses based on category, customer reviews, or location patterns.
When combined with enrichment tools and CRM automation, Google Maps data becomes a powerful source of master data for growth-oriented decisions.
Data Extraction Capabilities: What Information Can Be Retrieved
When it comes to Google Maps Scraping, understanding what kind of data you can extract is crucial. Whether you’re building a sales prospect list, conducting market research, or analyzing competition, the quality and depth of your data determine the value of your scraping efforts.
Fortunately, Google Maps provides an enormous pool of structured business information that can be automatically collected, cleaned, and exported into usable formats liek CSV, JSON, or Excel.
Basic Business Data
Google Maps scraping lets you capture all the essential business information that’s already visible on Google Maps listings.
Most Commonly Used Extracted Fields
| Data Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Business Name & Type | Identifies the company and its industry category. | “Sunrise Dental Clinic” – Dentist |
| Full Address & Location | Includes street, city, region, postal code, and country. | “123 Main St, Toronto, ON, Canada” |
| Phone Number & Website | Enables instant contact or outreach. | +1 (416) 555-0102 – www.sunrisedental.ca |
| Ratings & Review Counts | Shows social proof and brand credibility. | ⭐ 4.7 (120 reviews) |
| Review Text | Contains customer sentiment data for analysis. | “Excellent service and friendly staff.” |
| Operating Hours & Popular Times | Helps assess business activity levels. | “Open 9 AM – 6 PM” |
| Geo Coordinates (Latitude/Longitude) | Used for mapping, clustering, or distance-based targeting. | 43.651070 / -79.347015 |
| Google Place ID | Unique identifier for API and automation workflows. | ChIJN1t_tDeuEmsRUsoyG83frY4 |
| Photos & Price Range | Adds visual and contextual cues for product or service tier. | “$$ • Italian Restaurant” |
| Closure Status | Flags businesses as “Permanently Closed” or “Temporarily Closed.” | “Closed Permanently” |
Specialized Enriched Data
For advanced users and SaaS marketers, Google Maps scraping tools can go beyond public listings by integrating external APIs, enrichment engines, or AI-assisted models to expand the datasets.
Enriched Data Type
| Data Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Email Addresses & Outreach Details | Extracts emails and social links for sales outreach and CRM enrichment. | info@greenleafspa.com, facebook.com/greenleafspa |
| Social Media Profiles | Includes links to company’s Facebook, Instagram, or LinkedIn accounts. | linkedin.com/company/techhub |
| SEO Metadata | Gathers website meta titles, descriptions, and keywords for SEO analysis. | Title: “Affordable Dental Care | SmileBright Clinic” |
| Website Technologies | Detects CMS platforms, plugins, and scripts used on business websites. | WordPress, Elementor, Google Analytics |
| Advertising Pixels & Trackers | Identifies installed ad pixels like Meta Pixel or Google Ads tag for marketing insights. | Meta Pixel (fbq), Google Ads Tag (gtag.js) |
| Industry-Specific Attributes | Collects niche-specific data like gas prices, menu items, or service offerings. | “Regular: $3.45/gallon” or “Menu: Vegan Lunch Set” |
| Reviewer Details | Captures reviewer ID, profile status, and total number of reviews for sentiment studies. | User123 (Local Guide, 57 reviews) |
| Business Claiming Status | Indicates whether the business has claimed its Google listing. | Claimed / Unclaimed |
Why This Data Matters
Every field you scrape from Google Maps has a strategic use case:
- Addresses and coordinates → for mapping, delivery route optimization, or local SEO audits.
- Ratings and reviews → for sentiment analysis or quality benchmarking.
- Website and contact details → for direct outreach and B2B lead generation.
- Meta and tech data → for SaaS or MarTech sales targeting.
When properly combined and analyzed, these datasets reveal market gaps, customer behavior patterns, and growth opportunities that would otherwise remain invisible.
Methods for Data Extraction: Comparing Approaches
When it comes to Google Maps Scraping, not all extraction methods are created equal. Some are slow and limited by Google’s internal restrictions, while others allow you to scale your data collection efficiently and reliably.
This section breaks down the official Google methods versus automated scraping solutions, helping you choose the right approach based on your goals, technical ability, and project size.
Official Google Methods (Limitations for Scale)
While Google provides its own tools to access the Maps data, they’re not optimized for large-scale lead generation or data mining.
- Manual Search
- Each query typically shows no more than 120 results before pagination ends.
- Every search and copy-paste process must be done manually. This is painfully slow and error-prone.
- Even for small datasets, the manual approach can consume hours (or days) of repetitive work.
- Google Maps Places API: Google’s official API allows programmatic access to business data, but only to a very limited extent.
- Limited Results: Each API call returns a maximum of 20 results, and even with pagination, there’s a hard 60-result ceiling per query.
- High Costs: The free tier offers very few calls; once exceeded, fees apply based on volume. This can make large projects cost-prohibitive.
- Data Gaps: The API doesn’t expose critical outreach data such as email addresses, social media links, or professional networking site’s profiles, limiting its value for sales and marketing use cases.
Automated Scraping Solutions
Businesses that need speed, flexibility, and scale can often turn to automation tools. These platforms bypass manual collection by using scraping engines that extract structured data from Google Maps and export it into CSV, Excel, or JSON format, which is ready for analysis or CRM upload.
1. No-Code Solutions (Best for Beginners)
No-code scrapers are the most beginner-friendly approach to Google Maps scraping. You don’t need programming skills; simply enter your target query, and the tool does the rest.
- Popular Tools
- Outscraper
- Apify
- Octoparse
- ScraperAPI
- PhantomBuster
- How It Works (example)
- Go to your scrape dashboard
- Enter your search term (e.g., ‘bagel shops in New York’)
- Apply filters such as “minimum rating” or “must have website”
- Start the scrape (the tool automatically navigates Google Maps and collects data).
- Export your results to CSV, Excel, or JSON for further use.
2. Scraping APIs
For larger organizations or developers, Scraping APIs offer raw speed and scalability. These APIs are built for bulk extraction; they are capable of processing tens of thousands of results per hour. They handle pagination, proxy rotation, and anti-bot challenges automatically. Some of the No-Code tools providers also offers APIs.
- Top Providers
- Bright Data Google Maps Scraper
- Scrapingdog API
3. Chrome Extensions
If you only need to scrape a few hundred results, browser extensions can be quick and handy. However, they rely on your personal IP address, which means if you have too many requests, your browser can be temporarily blocked by Google.
It is perfect for freelancers or local marketers testing small data batches. This is not suitable for sustained large-volume extraction.
4. Custom Programming (e.g., Python)
For maximum flexibility, developers can build custom Google Maps scrapers using Python libraries like Requests, BeautifulSoup, or Selenium.
Pros:
- Full control over logic, fields, and export formats
- Ability to integrate with your CRM or database
Cons:
- Requires coding expertise
- Needs regular maintenance (Google updates HTML structure often)
- Must use proxies and rate-limiting to avoid IP bans.
Choosing the Right Scraping Methods
| Approach | Best For | Speed | Scale | Cost | Skill Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Search | Small one-time lookups | ❌ Slow | ❌ Very Limited | ✅ Free | ⭐ Beginner |
| Google Places API | Developers needing accurate geo data | ⚙️ Moderate | ⚙️ Moderate | 💰 Costly at scale | ⭐⭐ Intermediate |
| No-Code Tools | Marketers & SMBs | ✅ Fast | ✅ Large | 💰 Moderate | ⭐ Beginner |
| Scraping APIs | SaaS Platforms & Enterprises | 🚀 Very Fast | 🚀 Massive | 💰💰 Higher Cost | ⭐⭐⭐ Advanced |
| Custom Programming (Python) | Developers seeking full control | ⚙️ Fast | ✅ Customizable | 💰 Low (Time-intensive) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Expert |
Technical and Legal Compliance
Scraping Google Maps isn’t just plug-and-play. Google employs advanced anti-scraping systems to detect and limit automated data collection. This is just an overview for the popular question if Google Maps Scraping is Legal. Below are the key hurdles to overcome them responsibly:
1. Anti-Scraping Measures
Google’s systems identify suspicious behavior such as:
- Rapid requests from a single IP address.
- Unnatural scrolling or clicking patterns.
- Excessive queries in a short time frame.
If detected, your IP may be temporarily blocked — or worse, your Google account could get suspended.
2. Proxy Rotation: Your Safety Net
To mitigate this, proxy servers are essential:
- Datacenter proxies are cheaper and faster but can be detected more easily.
- Residential proxies use IPs from real users, offering greater authenticity and lower detection risk.
3. AI Utility in Scraping
While AI tools like ChatGPT or Copilot can’t directly scrape data (due to ethical and technical limits), they can:
- Generate custom Python or Node.js scraping scripts.
- Help debug scraper logic or optimize for efficiency.
- Automate data cleaning or enrichment workflows after scraping
Legal and Ethical Boundaries
Let’s clarify the gray area: Scraping Google Maps technically violates Google’s Terms of Service (ToS), which prohibits automated data extraction. However, legality depends on what and how you scrape.
1. Terms of Service Violation
Google’s ToS explicitly forbids the use of automated tools to extract data without prior consent.
Violations can lead to:
- API access suspension
- IP blacklisting
- Potential legal complaints in extreme cases
2. Public vs. Private Data
From a legal standpoint, scraping public business data (e.g., names, addresses, ratings) is generally permitted — provided the data remains accessible to anyone on Google Maps.
However, avoid collecting:
- Personal data (e.g., reviewer names, profile photos) without consent.
- Sensitive metadata (e.g., user tracking or behavioral insights)
3. GDPR and Data Privacy
Under the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR):
- You must have a legitimate reason for processing personal data.
- You should anonymize data wherever possible.
- Users must have the right to request deletion (“right to be forgotten”).
4. Best Practice Checklist
To stay compliant and ethical:
- ✅ Scrape only publicly available business data.
- ✅ Use rate-limiting and proxy rotation to avoid overloading servers.
- ✅ Respect robots.txt and local data protection laws.
- ✅ Avoid selling scraped data without consent or added value (e.g., enrichment or analytics).
Summary Table: Technical & Legal Compliance Overview
| Category | Key Issue | Best Practice / Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Technical | Anti-scraping detection by Google | Use rotating proxies and apply rate limits. |
| Technical | Proxy management | Use residential proxies for large-scale scraping. |
| Legal | Violation of Google’s Terms of Service | Consider APIs or compliant data providers. |
| Legal | Personal data under GDPR | Avoid scraping names, emails, or profile photos; anonymize data. |
| Ethical | Data misuse or resale | Use scraped data for insights, not raw resale; credit data sources. |
Conclusion: Driving Data-Informed Decisions
Google Maps scraping has emerged as one of the most efficient ways to collect real-world business intelligence in today’s hyper-localized marketing and precision-based business. It empowers decision-makers to see the bigger picture, while acting on granular insights that traditional data sources often miss.
Summary of Key Benefits
Google Maps scraping streamlines data collection, which will eliminate the need for manual searches or slow API calls. Businesses can now access real-time, location-based intelligence within minutes instead of days.
Here’s what that means in practice:
- Faster, Smarter Lead Generation: Build clean, verified prospect lists with accurate contact and location details.
- Comprehensive Market Research: Analyze local competition, market gaps, and business density patterns for better planning.
- Informed Business Strategy: Make data-driven decisions on expansion, pricing, or outreach using factual, map-based intelligence.
- Ease of Use: Even users without coding experience can benefit from no-code scraping platforms like Outscraper, Apify, or Octoparse.
Integrations and Future Outlook
The scraped data is exportable in universal, machine-readable formats such as:
- CSV or Excel: Ideal for sales and CRM imports.
- JSON or XML: Perfect for developers and automation platforms.
- Integrations: Directly connect with tools like Zapier, Make, Airbyte, or Power BI for analytics and automation.
This flexibility ensures scraped data flows seamlessly across your organization’s tech stack, from marketing automation to business intelligence dashboards.
As the global Location Intelligence market continues to grow, the ability to use Google Maps’ granular, real-world data will become an advantage. Businesses that embrace this technology early will be able to:
- Identify new market opportunities faster,
- Optimize logistics and on-ground presence, and
- Deliver hyper-localized customer experiences.
Thank You For Your Support!
If you want to dive deeper into various Google Maps Scraping topics, make sure to visit MapScraping.com regularly – your trusted authority for discovering the best tools, guides, and unbiased insights on Google Maps scraping.
Unlike other review sites, MapScraping is not sponsored by any scraping platform – ensuring all recommendations are based on real testing, practical use, and transparent evaluation.
Whether you’re a business owner, marketer, entrepreneur, or lead generation specialist, MapScraping.com will guide you in choosing the right tools for your scraping needs. We adhere to legal, ethical, efficient, and effective scraping.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Google Maps Scraping is the automated extraction of publicly available business data and Points of Interest from Google Maps. It is primarily used for Lead Generation, Market Research and Analysis.
You can extract a wide range of data, including:
Business names, categories, and phone numbers
Addresses and geographic coordinates (latitude/longitude)
Ratings, reviews, and operating hours
Website URLs, price ranges, and photos
Advanced tools can also extract enrichment data like:Emails, professional networking sties’ profiles, and social media links
SEO metadata (titles, descriptions, technologies used)
Reviewer IDs and sentiment analysis
Use a no-code scraping platform.
Here’s a simple workflow:
Go to your chosen tool (e.g., Outscraper or Octoparse).
Enter your search term (e.g., “salons in Chicago”).
Select filters like minimum rating or must-have website.
Start extraction, the tool automatically crawls listings.
Export your data as CSV or Excel for CRM upload.
No programming is needed, and most platforms handle proxy rotation and rate limits automatically.
Proxies prevent IP bans by rotating your connection between different IP addresses.
Datacenter proxies are fast and inexpensive, ideal for small projects.
Residential proxies use real-user IPs, offering higher success rates and lower detection risk for large-scale scraping.
Using proxies ensures smoother, uninterrupted scraping sessions.
AI can’t directly scrape data due to platform restrictions, but it can:
Generate Python or Node.js scraping scripts.
Automate data cleaning, deduplication, or enrichment.
Analyze scraped data for insights (e.g., sentiment trends or competitive gaps).
In short, AI acts as a co-pilot, enhancing scraping, not replacing it.
Scraped Google Maps data can power:
Local lead generation (find businesses by location or niche)
Competitor benchmarking (compare reviews, prices, ratings)
Hyper-local marketing campaigns (target by geography)
Market expansion planning (identify underserved areas)
It transforms public map data into actionable business intelligence.
Scraping publicly accessible data is generally legal. However, it explicitly violates Google’s Terms of Service (ToS). it is critical to use the data ethically and adhere strictly to Data Privacy laws (like GDPR/CCPA) when handling any personal information.
We are a curated directory where every Google maps scraper is vetted and recommended by experienced industry power users. We help you skip trial-and-error by comparing tools based on their data accuracy, reliability, and advanced features and benefits.

